Ready to Get Started
At Provance, we go out of our way to bring you great service. That’s in our digital DNA. Your IT success is our success.
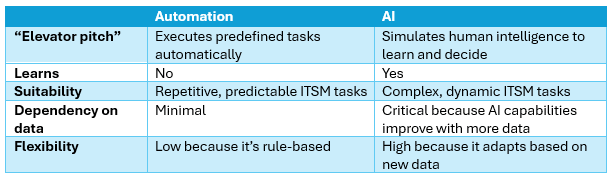
You might hear people using the terms “automation” and “artificial intelligence (AI)” interchangeably, but the two technologies are very different. While both will improve your IT organization’s services, operations, experiences, and outcomes, any IT service management (ITSM) professional looking to benefit from the technological advances being made in ITSM tools must understand the differences between automation and AI.
To help, this blog explains the fundamental differences between automation and AI, including how each technology helps ITSM and when they work well together.
Automation is the use of technology to perform tasks without human intervention. Importantly, automation is based on predefined rules, scripts, or workflows. It simply follows instructions. It doesn’t think, learn, or adapt beyond its programming.
A form of automation that’s commonly confused with AI is Robotic Process Automation (RPA), which uses “software robots” to mimic simple, repetitive human actions. ITSM examples of RPA use include:
So remember that this is automation, not AI, at work.
Automation excels at undertaking predictable, repetitive tasks. It usually replaces manual effort, time, and costs – for example:
All these automated activities help speed up tasks and reduce the reliance on (and cost of) human staff. However, automation has limitations – because no learning is involved, it is best suited to consistent, structured, high-volume activities where variation is minimal.
AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines. A key differentiator from automation is that AI involves the ability to:
So, AI doesn’t just follow pre-programmed steps. Instead, it analyzes information, adapts to new data, and improves over time.
While the umbrella term “AI” might be used, many flavors and variants are involved in AI ITSM use cases. While knowing the ITSM use case (and how it helps) is likely more beneficial than knowing about the different AI variants, it’s worth understanding some of the employed terminology. To start, there are:
Then, there are three AI terms in vogue in 2025:
As already mentioned, AI goes beyond the rote task execution of automation to add intelligence to your ITSM processes. For example:
Another way automation and AI capabilities are often characterized is through the terms “deterministic” and “non-deterministic,” respectively. Deterministic is where a process always produces the same output for a given input, while a non-deterministic algorithm can produce different outputs for the same input.
The title of the previous section, “Automation vs. AI,” is a little misleading because the two technologies and their ITSM opportunities aren’t mutually exclusive. Instead, they can work together to achieve the required IT operations and business outcomes. For example:
Combining automation and AI allows your IT organization to benefit from both technologies. Automation boosts operational efficiency and consistency, usually by eliminating manual work for routine tasks. While AI brings intelligence and adaptability. It’s important to use each technology where it excels. It’s a little like the adage of not using a screwdriver to hammer in nails.
To learn more how AI will help your IT operations and outcomes, check out these resources:
Blog Post: The Human Touch in AI Adoption
Blog Post: The Skillsets IT Service Desk Agents and Managers Need in the Age of AI
Blog Post: AI Driven ITSM: Pioneering Workload Management for the Future
Blog Post: Microsoft Copilot: The AI and Automation Opportunity for ITSM
Whitepaper: Cloud Lighthouse Crafting Your Future-Ready Enterprise AI Strategy
At Provance, we go out of our way to bring you great service. That’s in our digital DNA. Your IT success is our success.